6.23
Design a database for a worldwide package delivery company (e.g., DHL or FedEx). The database must be able to keep track of customers who ship items and customers who receive tiems; some customers may do both. Each package must be identifiable and trackable, so the database must be able to store the location of the package and its history of locations. Locations include trucks, planes, airports, and warehouses.
Your design should include an E-R diagram, a set of relational schemas, and a list of constraints, including primary-key and foreign-key constraints.
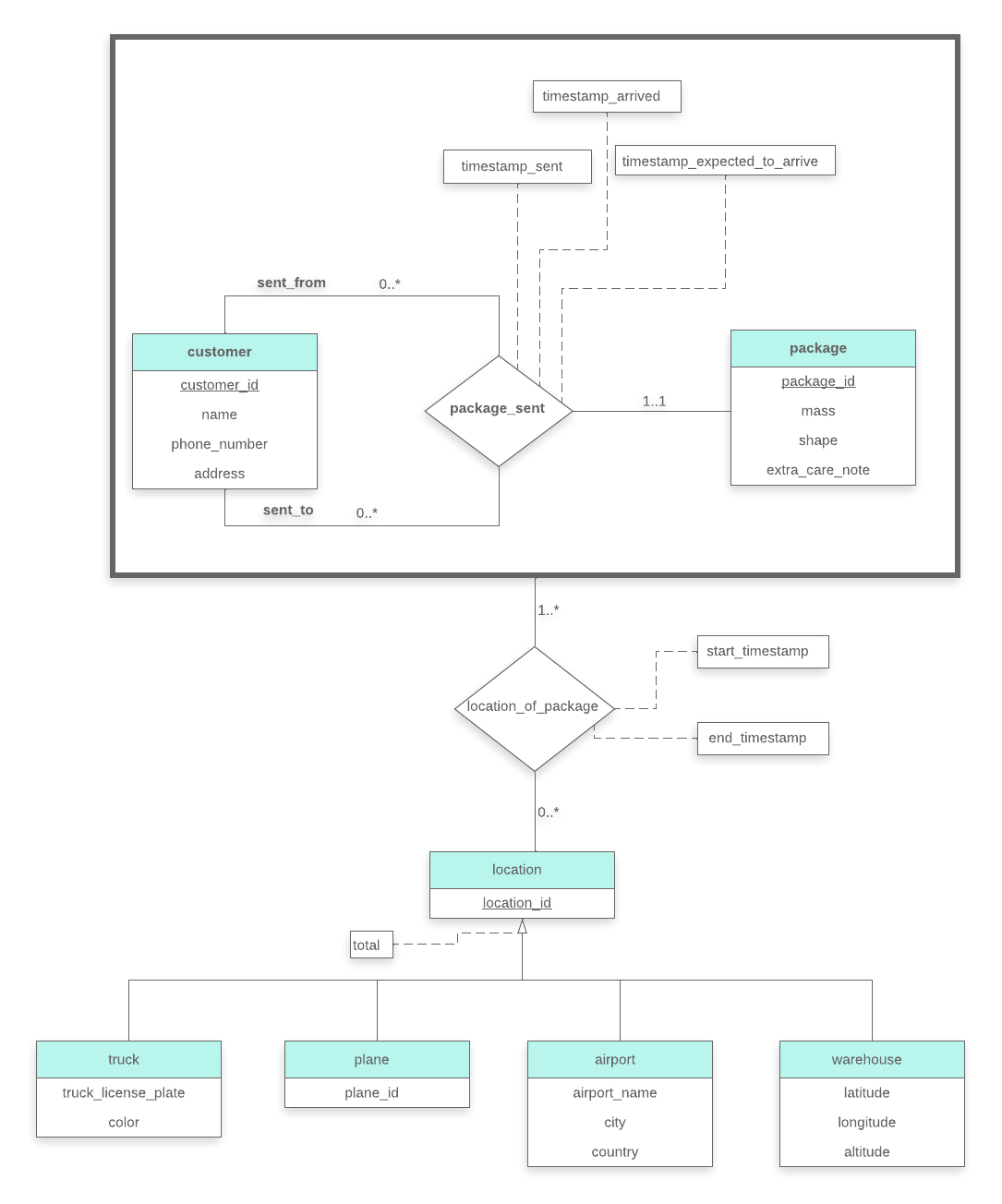
The above picture shows E-R diagram for the package delivery company. Note that it uses specialization/generalization and aggregation. Also the specialization is both total and disjoint.
Relation Schemas:
customer(customer_id, name, phone_number, address)
package(package_id,mass,shape,extra_care_note,sent_from,sent_to,timestamp_sent, timestamp_arrived,timestamp_expected_to_arrive)
location(location_id)
truck(location_id, truck_license_plate, color)
plane(location_id,plane_id)
airport(location_id,airport_name,city,country)
warehouse(location_id,latitude,longitude,altitude)
location_of_package(package_id, location_id, start_timestamp, end_timestamp)
Note that we have merged the relationship set package_sent and the entity set package when changing the E-R diagram to a relational schema above into the relation package.
The primary key of truck, plane, airport, and warehouse is location_id. Note also that their primary key is also a foreign key to the location relation.
Another foreign-key can be found in the package relation. Both sent_from and sent_to attributes are foreign-keys from the package relation referencing the customer relation.
The location_id of the relation location_of_packages references the location relation. The package_id of the relation location_of_packages references the package relation.