6.22
Design a database for an automobile company to provide to its dealers to assist them in maintaining customer records and dealer inventory and to assist sales staff in ordering cars.
Each vehicle is identified by a vehicle identification number (VIN). Each individual vehicle is a particular model of a particular brand offered by the company (e.g., the XF is a model of the car brand Jaguar of Tata Motors). Each model can be offered with a variety of options, but an individual car may have only some (or none) of the available options. The database needs to store information about models, brands, and options, as well as information about individual dealers, customers, and cars.
Your design should include an E-R diagram, a set of relational schemas, and a list of constraints, including primary-key and foreign-key constraints.
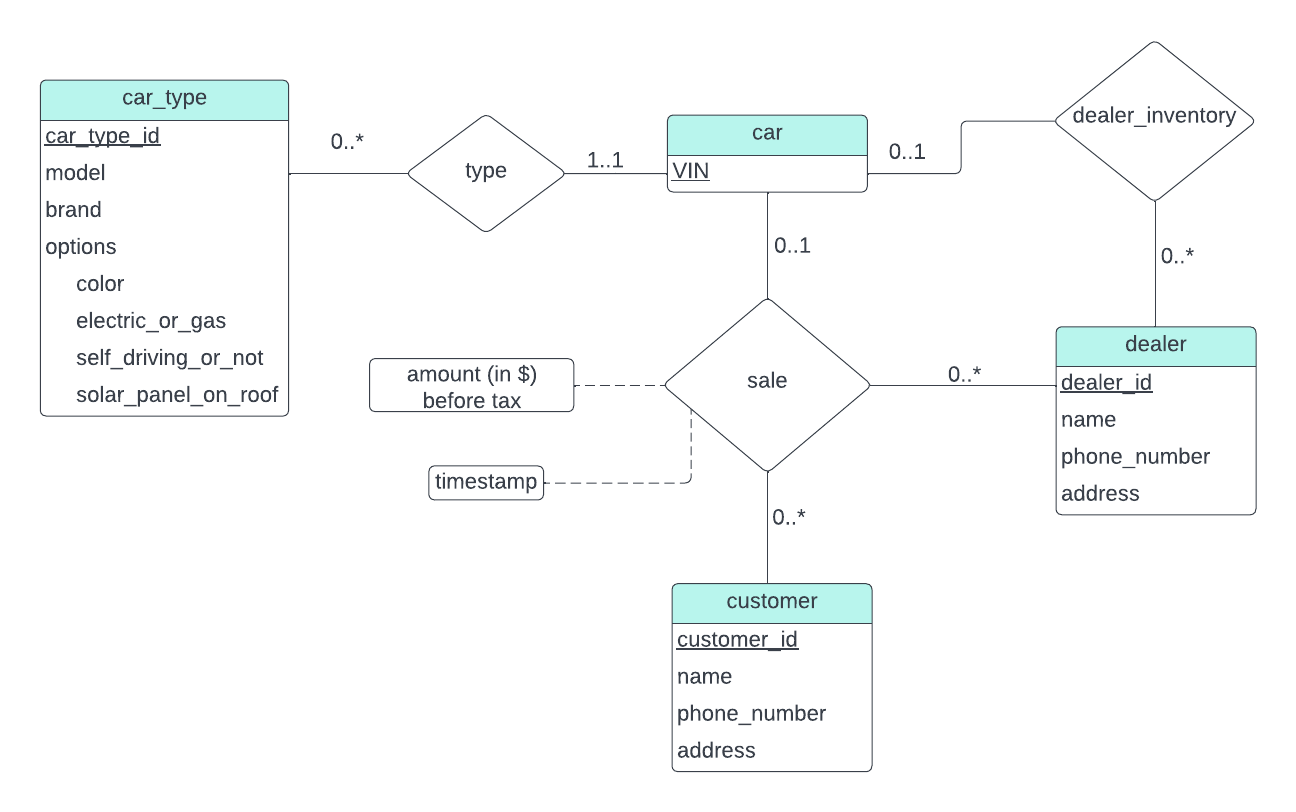
The above figure displays the E-R diagram of the database for the automobile company. The attribute options of the entity set car_type is a composite attribute. The ternary relationship set sales represents a single trasaction or a sale of a car. A dealer may have never sold a car or have sold numerous cars. A customer may have never bought a car or have bought numerous cars. But a particular car has either been sold or in stock. This constraints are represented as mapping cardinalities in the diagram.
When we change the diagram to a relational schema we get the following:
car_type(car_type_id, model, brand, color, electric_or_gas, self_driving_or_not,solar_panel_on_roof)
car(VIN, car_type_id, dealer_id)
customer(customer_id, name, phone_number, address)
dealer(dealer_id, name, phone_number, address)
sale(VIN, customer_id, dealer_id, amount, timestamp)
The attributes car_type_id and dealer_id in the relation car are foreign-keys referencing car_type and dealer relations respectively. The sale relation has VIN, customer_id and dealer_id as foreign-keys referencing the relations car_type, customer and dealer respectively.